How Gen AI Disrupts the SDLC
Contents
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Code Smells and Technical Debt
- Release and Productivity Pressures
- Refactoring: A Cornerstone of Digital Transformation
- Generative AI in Software Development
- Key Areas of Impact
- Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
- Applications of GenAI in Software Engineering
- Leveraging GenAI for Consistency and Productivity
- Research Insights on GenAI in SDLC
- Future Trends and Considerations
- Conclusion
- References
Executive Summary
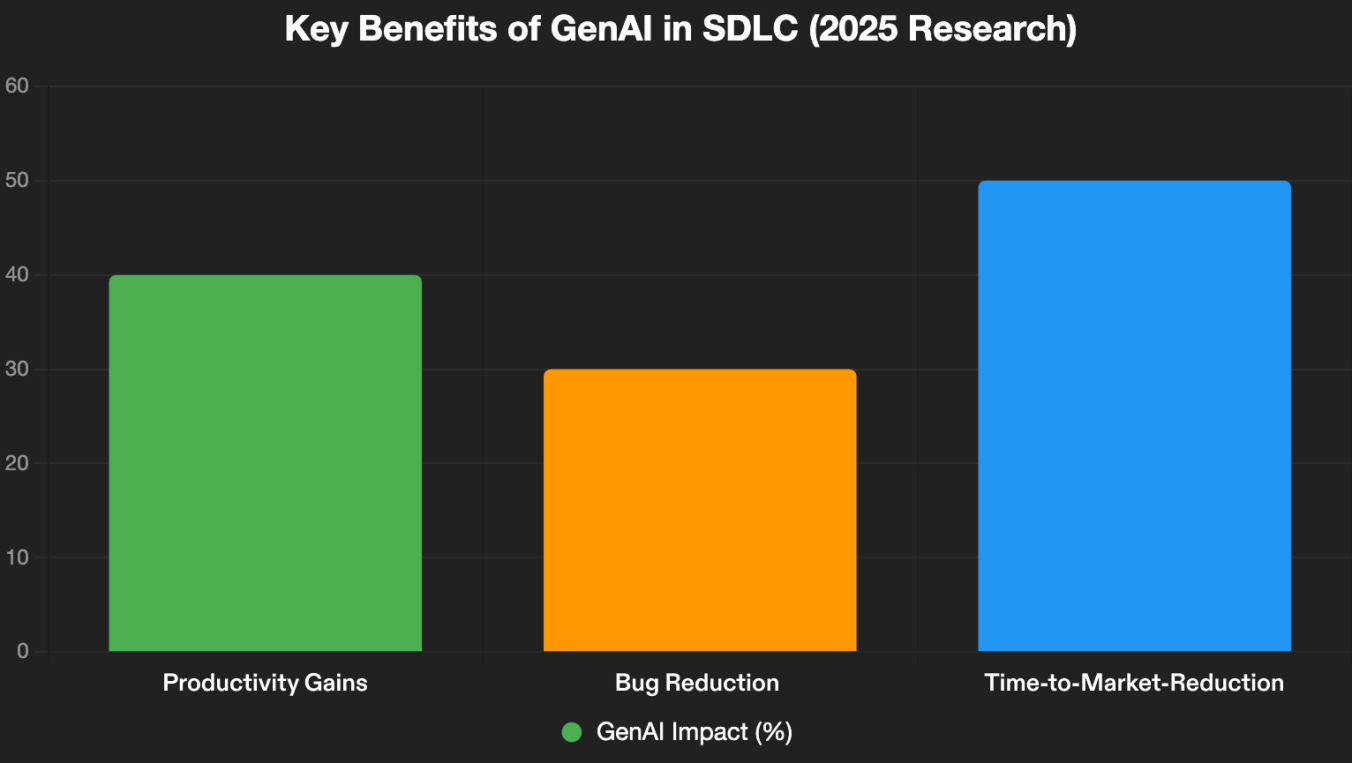
In 2025, generative AI (GenAI) is no longer an emerging technology—it's a core driver reshaping the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). As organizations grapple with technical debt costing up to 61 billion workdays annually, GenAI offers a pathway to automation, enhanced code quality, and accelerated innovation. This white paper, informed by the latest insights from McKinsey, Gartner, Forrester, and IDC, explores GenAI's disruptive potential across SDLC phases. Key findings include: up to 50% reductions in development time, 30% fewer bugs, and productivity gains for 75% of developers. Through case studies from Intuit, Alibaba, and GitLab, we illustrate real-world applications, urging leaders to integrate GenAI for sustainable software engineering.
Introduction
Serial tech entrepreneur and innovator Marc Andreessen observed more than a decade ago that "software is eating the world," a prescient statement made when digital transformation was still emerging and far from the ubiquitous buzzword it is today. Fast forward to 2025, and McKinsey's ongoing research affirms that "every company is a software company." Nearly 70 percent of top economic performers—compared to just half of their peers—are leveraging their own software to differentiate themselves from competitors, with fully one-third monetizing software directly. How do we even define Amazon in this landscape? It is the epitome of a software-driven empire, where algorithms and code orchestrate everything from logistics to personalized recommendations.
This profound shift has been accompanied by a seismic change in software development and delivery methodologies—the rise of Agile practices, marking a deliberate departure from the rigid, sequential traditional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). In today's hyper-competitive environment, the rapid creation and iterative delivery of software features is no longer optional; it is the linchpin for capturing and sustaining market advantage. Features must evolve swiftly to meet user demands, integrate with emerging technologies, and comply with an ever-expanding web of global regulations.
It is precisely within this high-stakes context that Generative AI (GenAI) emerges as the next disruptive force, poised to revolutionize software development by enabling unprecedented speed, efficiency, and quality. GenAI tools, powered by advanced large language models (LLMs), can now generate, refactor, and optimize code at scales previously unimaginable, addressing longstanding pain points in the SDLC. According to McKinsey's 2025 Global Survey on AI, organizations adopting AI-enabled software development processes are reporting up to 50% reductions in development time while enhancing output quality, fundamentally transforming how teams innovate and deploy. As Forrester Research aptly states, "Generative AI is transforming how software is developed, enabling rapid advancements and efficiencies that were once unimaginable."
Code Smells and Technical Debt
In the relentless pursuit of agility, businesses demand swift development and frequent rollouts to capitalize on fleeting competitive edges. However, this paradigm often breeds unintended consequences: a gradual erosion of code quality that undermines maintainability and, over time, hampers time-to-market velocity. As features are hastily added, evolved, and deployed amid tightening regulatory scrutiny—from data privacy laws like GDPR to industry-specific compliance standards—the codebase accumulates subtle flaws known as "code smells." These are not overt errors but insidious indicators of deeper structural weaknesses, such as overly complex methods, duplicated logic, or classes burdened with excessive responsibilities.
Consider a hastily applied hack to quash a recurring bug, the bloating of an already overcrowded class with yet another method, a lazy copy-paste of an existing class renamed for superficial uniqueness, an excessively long method that defies readability, or classes that hoard data without encapsulating meaningful behavior. Each of these represents a potential "smell" that signals code fragility, rendering it brittle and prone to cascading failures under future modifications. Left unchecked, these smells coalesce into "technical debt," a metaphor coined by Ward Cunningham, co-author of the Agile Manifesto. Technical debt manifests as an accumulating liability: the principal is the initial shortcut, and the interest accrues through escalating bugs, prolonged debugging sessions for obscure issues, and the cognitive overhead of deciphering convoluted logic. In 2025, global organizations are grappling with this burden acutely; CAST's "Coding in the Red" report estimates that technical debt equates to a staggering 61 billion lost workdays annually in software remediation alone, costing trillions in productivity and opportunity. Moreover, Protiviti's surveys reveal that firms allocate a full 30% of their IT budgets—averaging 20% of total resources—to managing this debt, diverting funds from innovation to mere survival.
Release and Productivity Pressures
Intuition might suggest that code smells and technical debt are predominantly the domain of novice developers fumbling through unfamiliar terrain. However, empirical evidence paints a more nuanced picture: even seasoned engineers introduce these issues when confronted with intricate, high-pressure tasks. A seminal study analyzing commit histories across three major open-source ecosystems—Apache, Eclipse, and Android—uncovered that 89% to 98% of code smells are injected in the frantic month leading up to a major release. This "final rush to release" phenomenon, driven by deadlines and stakeholder expectations, overrides best practices, prioritizing velocity over vigilance. The research, which scrutinized thousands of commits, highlighted that complexity, not inexperience, is the culprit—developers under duress opt for expedient solutions that accrue debt, perpetuating a vicious cycle.
In 2025, these pressures are amplified by the explosion of AI-driven tools, which, while accelerating coding, can inadvertently exacerbate debt if not governed properly. McKinsey reports that technical debt now consumes up to 40% of technology estates, slowing innovation and inflating costs. Clearly, software development stands to gain immensely from fortified coding practices, rigorous peer reviews, and intelligent automation. GenAI emerges here as a game-changer, embedding proactive quality checks into workflows to curb debt at its source.
| Pressure Factor | Impact Description | GenAI Countermeasure | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Release Rushes | 89-98% smells introduced in final month | Real-time smell detection via AI analyzers | 30% bug reduction |
| Resource Allocation | 30% IT budgets on debt management | Automated refactoring suggestions | 20-40% cost savings |
| Developer Experience | Seasoned devs falter on complex tasks | AI-assisted code guidance | 2x happiness boost |
Refactoring: A Cornerstone of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation thrives on the pillars of open standards, scalable cloud architectures, and seamless integrations—principles that render legacy systems obsolete in the face of modern demands for connectivity, elasticity, and ironclad security. Cloud platforms now rival or surpass the robustness of monolithic mainframes, offering unparalleled opportunities for faster, more agile integrations with a vast ecosystem of technologies. At the core of these endeavors lies refactoring: the disciplined restructuring of existing code to align with contemporary architectural paradigms, such as microservices or event-driven designs, without disrupting functionality. Whether embarking on legacy modernization, orchestrating cloud migrations, or weaving in cloud-native solutions, refactoring is indispensable. Its ultimate aim? To excise technical and technological debt, fostering systems that are resilient, extensible, and future-proof.
Clean, maintainable, and efficient code is the hallmark of successful refactoring, propelled by a triad of practices:
- Code Review and Static Analysis: Systematic scrutiny to unearth and eradicate code smells, ensuring early intervention before issues metastasize.
- Standards-Enforcing Templates: Pre-built scaffolds that impose coding conventions, promoting modularity and hygiene from inception.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Inline annotations and architectural blueprints that illuminate intent, easing onboarding and modifications for diverse teams.
In 2025, with IDC projecting up to 50% performance uplifts from cloud-refactored applications, refactoring transcends maintenance—it's a strategic imperative for digital agility.
Future Fast Forward: Generative AI in Software Development
Generative AI encompasses sophisticated systems that conjure text, imagery, and multimedia from natural language prompts, mimicking human creativity at machine speeds. Within software engineering, GenAI automates swaths of the SDLC—from nascent code synthesis to rigorous testing and fluid deployment—dismantling entrenched bottlenecks. By infusing intelligence into mundane workflows, it liberates developers to tackle visionary challenges, as evidenced by Gartner's 2025 prediction that 80% of application development will incorporate GenAI code generation by year-end.
Key Areas of Impact
GenAI's tentacles extend across the SDLC, yielding transformative efficiencies:
Code Generation:
- Automated Code Writing: GenAI crafts bespoke snippets or full modules from high-level specifications, slashing coding timelines by automating boilerplate and scaffolding. Developers describe requirements in plain English—e.g., "Implement a secure user authentication endpoint with JWT"—and receive production-ready code infused with security best practices.
- Boilerplate Code Automation: Tedious repetitive structures, like configuration files or CRUD operations, are generated instantaneously, freeing cognitive bandwidth for intricate business logic and innovation.
Test Case Creation and Execution:
- Automated Test Script Generation: AI derives comprehensive test suites from code diffs or requirements, bolstering coverage for edge cases and regressions while minimizing manual scripting—reducing test authoring time by up to 70%, per IDC benchmarks.
- Continuous Testing Integration: Seamlessly embeds into CI/CD pipelines, delivering instantaneous feedback on commits to preempt defects and accelerate iterations.
User Experience (UX) Design:
- AI-Driven Prototyping and Design: Synthesizes interactive wireframes and prototypes from user stories or feedback loops, iterating designs in real-time to align with accessibility and usability standards.
- Personalization: Dynamically tailors UI elements to user personas, leveraging behavioral data for hyper-relevant experiences that elevate satisfaction and retention.
Deployment and DevOps:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Autonomates IaC script creation for Terraform or Ansible, guaranteeing idempotent, reproducible environments that mitigate deployment drift and human error.
Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
Beyond creation, GenAI fortifies the post-deployment phase by anticipating failures and streamlining upkeep. It predicts latent issues in live applications through anomaly detection in logs and metrics, empowering proactive interventions that avert outages. In coding and delivery, GenAI excels by scrutinizing codebases for inefficiencies and prescribing enhancements:
- Analyzing sprawling repositories to pinpoint legacy patterns and recommend modular rewrites.
- Identifying obsolete libraries or inefficient algorithms, then generating performant alternatives.
- Suggesting targeted refactoring techniques, such as extracting methods or applying design patterns, to amplify speed and scalability.
- Restructuring codebases sans behavioral alterations, preserving APIs while internalizing improvements.
- Disentangling business logic from legacy monoliths, decoupling dependencies to facilitate microservices migration.
IDC's 2025 analyses confirm that cloud-refactored apps via GenAI achieve up to 50% performance gains, underscoring its role in sustainable operations.
Refactoring and Other Applications of GenAI in Software Engineering
GenAI's prowess in refactoring extends to broader engineering paradigms, catalyzing modernization, optimization, and cloud adoption.
1. Modernization
Modernization tops IT agendas, with Gartner noting 60% of leaders deeming it critical for investment, while McKinsey estimates up to 20% IT cost reductions for firms revitalizing legacy systems. In a landscape where outdated codebases stifle agility, GenAI streamlines refactoring and rewriting, automating the extraction of value from COBOL relics or Java monoliths into containerized, API-first architectures.
Case Study: Intuit's AI-Integrated Code Quality
Intuit grappled with codebase sprawl across TurboTax and QuickBooks, where complexity bred technical debt and throttled cycles. By embedding GenAI into its GenOS platform—launched in 2025 with AI Workbench and domain-specific LLMs—Intuit now analyzes code for vulnerabilities, suggests compliant improvements, and learns from historical reviews. This has slashed debt, accelerated velocity by 30%, and democratized AI-assisted generation, ensuring adherence to Intuit's APIs and standards.
2. Refactoring
McKinsey's 2025 study reveals 50% of development efforts orbit refactoring for sustainment and performance; GenAI supercharges this by unearthing inefficiencies and proffering optimal strategies, from dead code elimination to concurrency enhancements.
Case Study: Alibaba's AI-Enhanced Code Reviews
Alibaba's meteoric expansion overwhelmed manual reviews, inflating risks and delays. In 2025, its Qwen3-Coder model—Alibaba's flagship open-source AI coder—now dissects pull requests for smells, automates feedback on architecture and security, and integrates with IDEs for real-time nudges. This has expedited reviews by 50%, elevated quality, and amplified productivity, powering Alibaba's 90% YTD stock surge on AI momentum.
3. Cloud-Native Application Development
Gartner's 2025 insights project 40% total ownership cost cuts via cloud-native apps; GenAI hastens this by auto-generating Kubernetes manifests and serverless functions, embedding resilience from the ground up.
Case Study: GitLab's Cloud-Native Acceleration
GitLab harnesses GenAI in its 18.4 release (2025) for AI-native pipelines, automating vulnerability scans, code suggestions, and CI/CD orchestration. As a Leader in Gartner's 2025 Magic Quadrant for AI Code Assistants, GitLab's Duo suite detects issues pre-merge, fortifies cloud-native security, and sustains 1st-place rankings in four use cases—yielding faster, more reliable releases with 25% efficiency gains.
Leveraging GenAI for Consistency and Productivity
Harnessing GenAI for code reviews, refactoring, and standards enforcement cultivates enterprise-wide uniformity: shared paradigms for recurrent challenges, standardized structures, self-explanatory code, and rigorous testing—transcending individual variances. This uniformity bolsters maintainability while turbocharging output. Optimal GenAI deployment liberates developers from drudgery—boilerplate scripting, bug hunts, documentation—redirecting energies to high-impact pursuits like novel features. Consequently, teams achieve compressed cycles, denser releases with more functionalities, and granular, frequent evolutions. IDC's 2025 Developer Trends Survey reports 75% of users experiencing productivity surges from AI coding aids.
Research Insights on GenAI in SDLC
Contemporary studies illuminate GenAI's seismic potential in software engineering:
- Enhanced Productivity: IDC's 2025 assessments show GenAI tools automate routines and furnish astute suggestions, yielding marked developer gains; Gartner forecasts 80% AI-assisted app development by 2025.
- Improved Code Quality: By weaving in best practices, AI code adheres to elevated standards, curbing maintainability woes. Forrester's 2025 Developer Survey highlights up to 30% fewer bugs and errors from AI tools.
- Faster Time-to-Market: GenAI propels SDLC stages, hastening product launches. McKinsey notes firms harnessing AI halve development durations.
Future Trends and Considerations
GenAI's trajectory promises deeper SDLC entwinement:
- Integration with DevOps: Tighter GenAI-DevOps fusion will automate pipelines holistically, from genesis to surveillance, per Gartner's 2025 trends.
- Advanced Debugging and Error Detection: GenAI will expedite bug triage, slashing resolution times by 40%, as Forrester predicts.
- AI-Augmented Collaboration: Real-time insights from aggregated data will amplify team synergy, boosting productivity 20-30%, McKinsey estimates.
Conclusion
Generative AI is inexorably disrupting the software development landscape, inaugurating an epoch of expeditious, superior engineering. By automating tedium, elevating code integrity, and galvanizing collaboration, GenAI equips organizations to surmount SDLC hurdles with finesse. As maturation accelerates, visionary leaders must proactively adopt these innovations to harness GenAI's full potency—ensuring not just survival, but supremacy in a code-pervasive future.


 AI Chatbot Development Company
AI Chatbot Development Company AI Software Development Solutions
AI Software Development Solutions Custom NLP Solutions
Custom NLP Solutions Generative AI Development
Generative AI Development Machine Learning Consulting Services
Machine Learning Consulting Services MLOps Consulting Services
MLOps Consulting Services














