AI-Powered Remote Patient Monitoring: Revolutionizing Healthcare Delivery in 2025 and Beyond
Contents
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- The Growing Crisis in Healthcare Delivery
- Understanding Remote Patient Monitoring
- The Role of AI in Transforming RPM
- Essential Technologies Supporting AI in RPM
- Practical Applications of AI in RPM
- Real-World Case Studies and Evidence
- Overcoming Challenges in AI-Driven RPM
- Future Trends Shaping AI in RPM
- Conclusion and Actionable Steps
- References
Executive Summary
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) empowers healthcare teams to track vital health metrics from afar, using accessible tools like smartphones and wearables. When integrated with artificial intelligence (AI), RPM evolves from passive data gathering into an active partner in care delivering predictive insights, personalized recommendations, and timely interventions that keep patients healthier and systems more efficient. This approach is particularly vital for conversational AI elements, such as voice-based check-ins, which enhance engagement without requiring screens or apps.
Today’s healthcare landscape is strained by escalating demands: an aging global population projected to double those over 60 by 2050 (from 12% to 22%), chronic diseases accounting for 74% of deaths and 90% of U.S. healthcare spending (over $4.5 trillion annually), and workforce shortages that could leave 10-15 million positions unfilled worldwide by 2030. AI addresses these by analyzing vast datasets in real-time, flagging subtle risks like early sepsis or irregular heart rhythms with up to 90% accuracy, and reducing hospital readmissions by 30-70% in pilots.
Drawing from 2025 research, including NIH reviews on AI-telemedicine integration, FDA-cleared tools like CLEWICU for ICU predictions, and reports on conversational AI’s role in RPM (e.g., 8.8% CAGR in adoption to $110 billion by 2027), this whitepaper provides an in-depth look at RPM’s transformation. We examine the crisis driving adoption, RPM fundamentals, AI’s core mechanisms with ethical voice tech considerations, supporting technologies including IoT and blockchain, expanded applications with evidence from biomarker analysis and activity classification, detailed case studies across chronic and acute care, multifaceted challenges with solutions like federated learning, and forward-looking trends like generative AI for virtual coaching.
For clinicians, developers, and leaders, this resource offers practical frameworks, data-driven examples (e.g., AI’s impact on vital signs monitoring and chronic disease trends), and steps to implement AI-RPM, fostering equitable, cost-effective care. The RPM market, valued at $10-12 billion in 2025, is on track to reach $60-100 billion by 2030, with AI comprising 40% of growth through enhanced remote monitoring and predictive analytics.
The global RPM market is expected to hit $175 billion by 2030, with AI driving a 12% annual growth rate, thanks to better tools for early warnings and personalized care. Let’s build a future where care is accessible, efficient, and personal.
Introduction
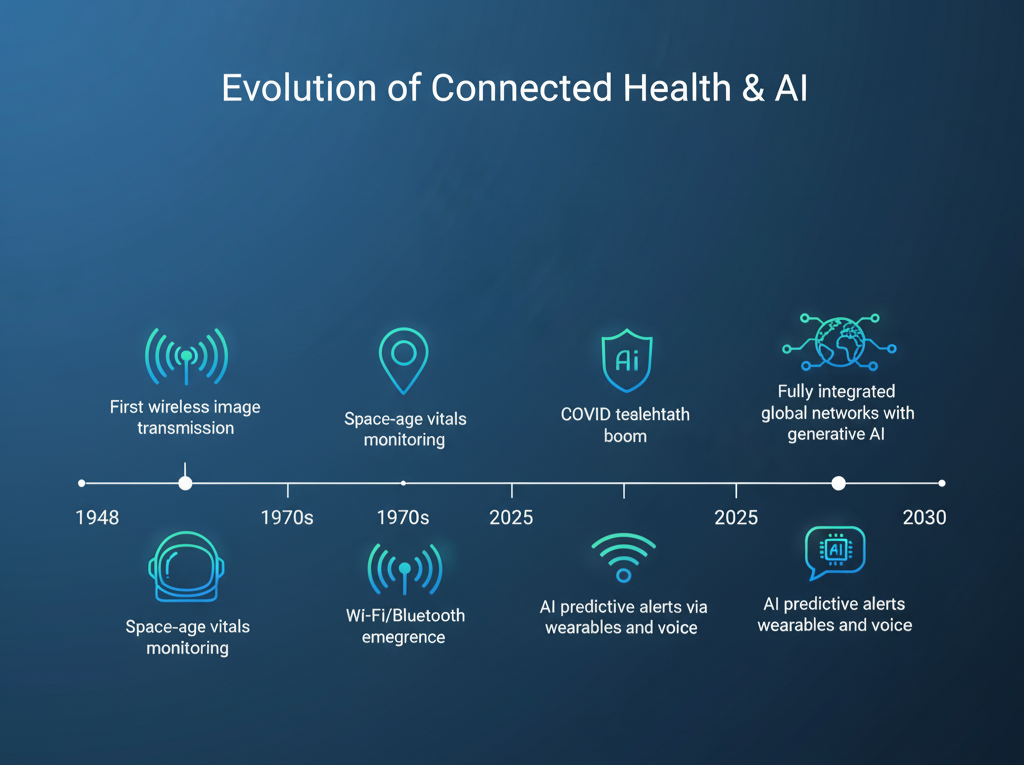
The roots of remote patient monitoring trace back to the mid-20th century—think 1948’s transmission of X-ray images over telephone lines or the 1960s monitoring of astronauts’ blood pressure from Earth. These early feats laid the groundwork for today’s sophisticated systems. Fast-forward to 2025: RPM leverages everyday tech like smartwatches and voice assistants, amplified by AI, to deliver care that’s proactive, not just reactive. Conversational AI, in particular, adds a human-like touch, using natural language to guide patients through symptom reporting or adherence reminders.
Consider a patient recovering from heart surgery in a rural area. Traditional follow-ups mean long drives or delayed calls. With AI-RPM, a wearable tracks heart rate and activity; AI detects anomalies, like a subtle arrhythmia, and sends an alert with tailored advice via voice preventing a trip to the ER. This isn’t futuristic; it’s routine in many U.S. hospitals, where RPM adoption surged 38-fold during COVID and now serves 71 million adults (26% of the population).
Yet, urgency defines this moment. Chronic conditions claim 41 million lives yearly, while provider shortages loom large up to 120,000 physicians short in the U.S. by 2036. AI bridges these gaps by processing terabytes of data to forecast risks, personalize plans, and extend care to underserved groups, including through voice biomarkers for early mental health detection. Drawing from 2025 NIH analyses on AI-telemedicine and FDA insights into adaptive models, plus reports emphasizing conversational AI’s role in RPM for inclusivity, this whitepaper demystifies AI-RPM.
We start with the crisis, unpack RPM basics, detail AI’s toolkit with a focus on ethical voice integration, explore tech foundations inspired by multi-layer architectures, dive into applications with metrics from biomarker analysis and activity classification, showcase diverse cases, confront barriers head-on with risk mitigation guidance, and forecast trends to 2030. Each section includes real data, visuals, and tips for adoption—empowering you to build resilient health ecosystems.
The Growing Crisis in Healthcare Delivery
Healthcare systems worldwide are buckling under interconnected pressures. Demand outstrips supply, costs spiral, and inequities deepen—making AI-enhanced RPM not a luxury, but a necessity for sustainable care. This crisis is ever-widening, as demographic shifts and socio-economic factors accelerate the need for inclusive, low-cost solutions like voice-enabled monitoring.
Workforce Shortages
The human element is healthcare’s backbone, yet cracks are showing. In the U.S., the Association of American Medical Colleges forecasts a shortfall of 37,800 to 124,000 physicians by 2034, with primary care facing up to 48,000 gaps—exacerbated by retirements, burnout, and post-pandemic exits. Globally, the WHO predicts 10-15 million unfilled roles in hospitals and home care by 2030, hitting low-resource regions hardest, where rural clinics operate at 50% capacity. Nurses and aides fare no better; turnover rates exceed 20% in many areas, delaying care and raising error risks by 15%.
AI-RPM eases this by automating routine tasks. Algorithms triage vitals, prioritizing urgent cases and slashing review time by 40%. A 2025 NIH study on AI-telemedicine found such systems let providers manage 25% more patients without added hours, preserving focus for empathy-driven interactions. Early adoption in U.S. clinics has correlated with 15% lower burnout scores among staff, while conversational AI handles patient queries, freeing 30% of call center time.
Rise of Chronic Diseases
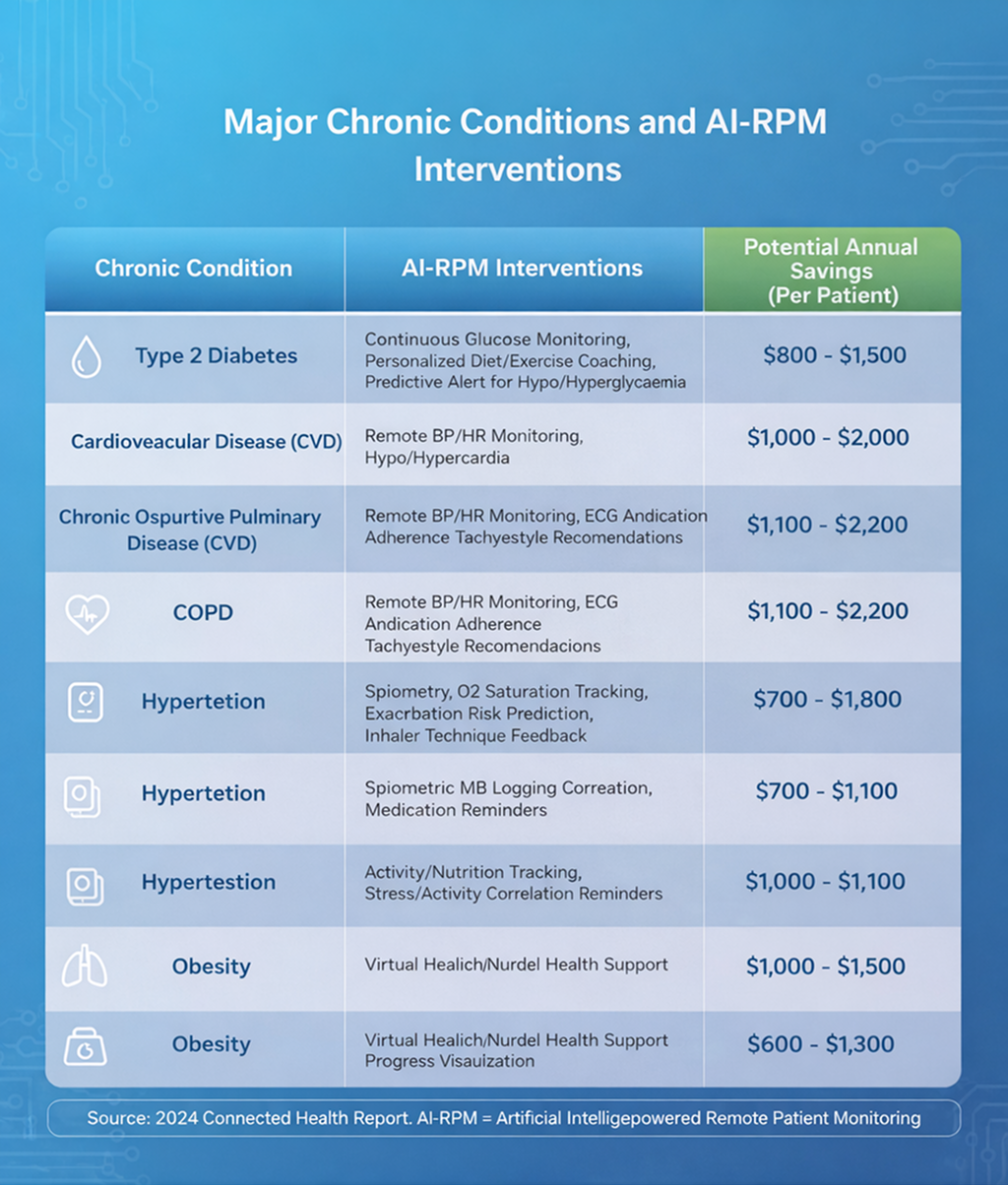
Chronic illnesses aren’t episodic—they’re relentless, affecting daily life and economies. By 2025, 75% of adults in developed nations grapple with at least one, from diabetes (537 million cases) to cardiovascular disease (523 million). These drive 74% of global deaths and 86% of U.S. healthcare dollars, totaling $4 trillion yearly—much from preventable complications like uncontrolled blood sugar or hypertension flares. The epidemic costs 86% of U.S. budgets toward chronic care alone.
Aging fuels the fire: The over-65 crowd will comprise 22% of the world by 2050, doubling care needs and increasing RPM demand for home-based tracking. AI-RPM counters this with continuous tracking; for instance, predictive models analyze trends to adjust insulin doses preemptively, improving A1C levels by 1.5 points and cutting events by 25%. Long-term, this shifts care from crisis response to prevention, potentially saving $300 billion globally by 2030 through biomarker-led interventions.
| Condition | Global Cases (2025 Est.) | Economic Burden | AI-RPM Intervention Example | Projected Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | 537 million | $1T/year | Glucose trend forecasting via wearables and voice prompts | 20% reduction in hospitalizations |
| Heart Disease | 523 million | $1.2T/year | Arrhythmia alerts reducing readmits 30% | $50B annually in U.S |
| COPD | 384 million | $50B/year (U.S.) | Breathing pattern analysis for exacerbations | 25% fewer ER visits via early voice detection |
Access and Equity Gaps
Equity remains elusive. Rural U.S. areas lack 20% of needed providers, while urban minorities encounter barriers like language or bias—leaving 83 million in medically underserved zones, including migrant communities and reservations. The digital divide compounds this: Only 70% of low-income households have broadband, dropping to 57% for those under $30,000 income, versus 92% for wealthier ones. Globally, 5 vulnerable populations (chronically ill, low-income, rural, LGBTQ+, elderly) face high poverty and infant mortality.
Conversational AI levels the field, using voice interfaces for non-tech-savvy users—no apps required. A 2025 WHO report highlights how simple phone-based RPM reaches 80% more isolated elders, detecting depression via speech patterns and linking to virtual support. This inclusivity not only closes gaps but boosts outcomes, with equitable AI tools showing 20% higher adherence in diverse groups, especially through culturally sensitive voice responses.
- Rural Challenges: Scarce facilities; AI enables geocode-based alerts.
- Minority Disparities: Bias in data; diverse voice datasets reduce errors by 25%.
Understanding Remote Patient Monitoring
RPM democratizes care by shifting focus from place-based visits to data-driven oversight. At its core, it’s about empowering patients and providers with timely, actionable information, often enhanced by conversational elements for natural interaction.
Core Components of RPM
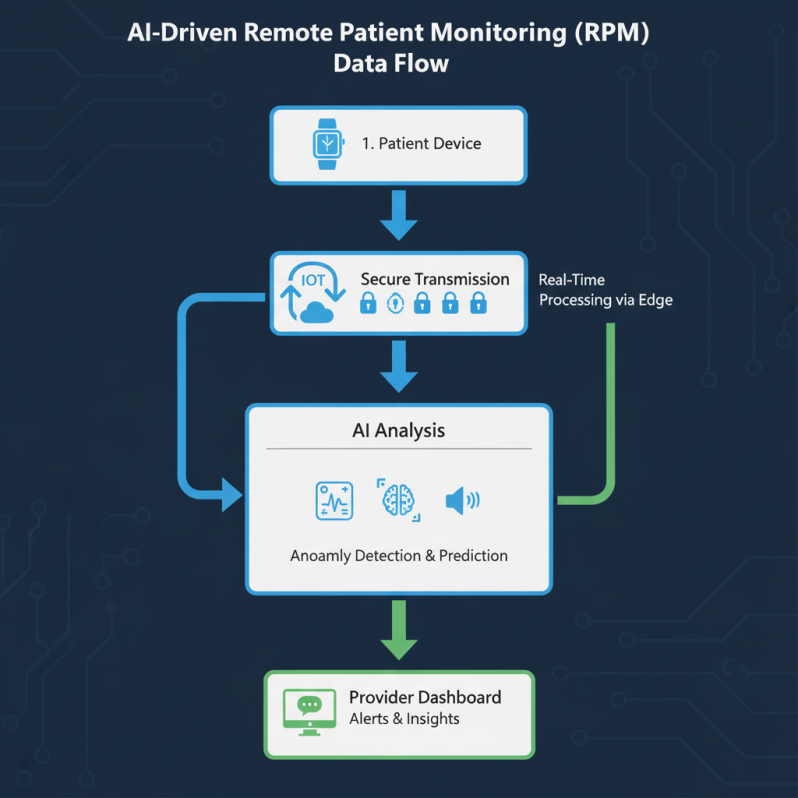
RPM ecosystems blend hardware, software, and human elements. Devices range from FDA-cleared wearables (e.g., ECG-enabled watches for arrhythmia detection) to home hubs for blood pressure cuffs and voice-activated scales. Data flows securely via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to apps or clouds, where it’s aggregated—vitals like oxygen saturation alongside self-reported symptoms or voice-recorded pain levels.
Transmission prioritizes encryption; standards like HL7 FHIR ensure interoperability with electronic health records (EHRs), allowing seamless sharing across providers. Analysis layers add value: Basic dashboards for trends, advanced AI for predictions like deterioration risks. Feedback closes the loop—patient apps deliver nudges like “Hydrate now” or provider alerts for escalations, with voice synthesis for accessibility. In 2025, hybrid models (passive sensors + active inputs) dominate, engaging 70% more users than passive-only setups, as they incorporate natural language for daily check-ins.
- Passive vs. Active: Sensors auto-collect; voice prompts encourage input.
- Scalability: Handles 1,000+ patients per system with cloud backups.
Evolution from Traditional to AI-Enhanced
Early RPM was labor-intensive: 1970s phone logs or wired monitors for reservation programs. The 2000s brought wireless leaps via Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, but siloed data limited impact. COVID catalyzed change, expanding Medicare reimbursements (e.g., CPT codes for RPM) and spiking usage—from niche to mainstream, with 26% U.S. adoption and global forecasts of 8.8% CAGR.
AI marks the pivot: From descriptive reports to prescriptive actions, incorporating deep learning for activity classification and NLP for voice analysis. A 2025 PubMed review notes AI cuts ER visits by 25% through early flagging, while generative models now simulate scenarios for training. This evolution promises 50% clinic integration by 2030, blending RPM with telehealth for seamless care, including SaMD clearance for voice tools.
The Role of AI in Transforming RPM
AI infuses RPM with intelligence, turning raw metrics into foresight. It’s the difference between knowing a patient’s heart rate spiked and understanding why—and what to do next—while ensuring ethical use through trustmarks like those for conversational AI.
Key AI Techniques Explained
AI’s arsenal is diverse and evolving. Machine learning (ML) excels in supervised tasks, like classifying heart rhythms with 95% precision using labeled datasets from wearables. Deep learning dives deeper, employing neural networks for video-based gait analysis to detect Parkinson’s tremors early, processing complex patterns in real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP) parses voice or text for nuances—e.g., stress indicators in daily check-ins, identifying biomarkers like vocal tremors for mental health. Reinforcement learning adapts dynamically, refining exercise plans for COPD patients based on response feedback and activity data. Federated learning preserves privacy, training models across devices without centralizing sensitive data, ideal for distributed RPM.
In 2025, generative AI (GenAI) emerges as a standout: Tools like enhanced large language models create bespoke care narratives from vitals, cutting documentation time by 50% and improving patient comprehension with voice-generated summaries. These techniques, often combined in hybrid architectures, handle complex, multimodal data—vitals, images, behaviors, and voice—for holistic insights, as seen in fog-edge setups for low-latency alerts.
- Supervised ML Example: ECG classification for arrhythmias.
- Unsupervised Deep Learning: Anomaly detection in breathing patterns.
Benefits for Patients, Providers, and Systems
Patients gain autonomy: Real-time feedback fosters adherence, with AI nudges boosting medication compliance by 35% and voice coaching reducing isolation. Providers save time—AI automates 80% of routine reviews, allowing focus on high-touch care and reducing burnout by 15%. Systems reap efficiency: Costs drop $2,000-10,000 per patient annually through fewer admissions; a 2025 NCBI analysis projects $300 billion in global savings by 2030 via predictive monitoring.
Equity improves too, with voice AI reaching non-digital users, narrowing outcome disparities by 20% in underserved populations. Overall, AI-RPM drives better outcomes with enhanced efficiencies, as early implementations show across clinical use cases.
Essential Technologies Supporting AI in RPM
AI-RPM’s power stems from a layered tech stack, ensuring seamless, secure data handling at scale, much like the multi-tier architectures in recent reviews.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Wearables
IoT devices—over 50 billion connected by 2025—form the frontline, capturing non-invasive metrics like pulse oximetry or motion via patches and bands. Wearables like Apple Watch or Dexcom G7 shine for continuous glucose monitoring, with AI filtering noise for 98% reliability and integrating voice for hands-free logging.
Challenges include battery drain and motion artifacts, addressed by edge AI for on-device processing. A 2025 FDA report praises these for expanding access, noting 40% uptake in chronic care, especially when paired with Bluetooth for low-power voice transmission.
- Non-Invasive Focus: No skin contact needed for many sensors.
- Integration Tip: Use APIs for EHR syncing.
Cloud, Edge, and Fog Computing
Cloud platforms (e.g., AWS or Azure Health) store petabytes for population-level analytics, enabling federated models across hospitals. Edge computing processes locally for millisecond alerts—crucial in remote areas with spotty connectivity, handling vital signs classification on-device.
Fog acts as a bridge, aggregating edge data before cloud upload, balancing latency and bandwidth for applications like emergency event detection. This hybrid handles 1TB+ daily from 1,000 patients, supporting real-time sepsis predictions with 85% sensitivity, as in blockchain-secured fog nodes.
Practical Applications of AI in RPM
AI’s versatility shines in targeted uses, from routine checks to life-saving alerts, backed by robust evidence and inspired by current implementations like voice for education and biomarker analysis.
Vital Signs and Emergency Detection
AI monitors ECG, SpO2, and BP, predicting deteriorations like sepsis 24 hours ahead with 90% accuracy via deep learning on multimodal data from IoT. In ERs, models integrate vitals for hemodynamic warnings, cutting response times by 30% and enabling non-invasive remote triage.
A 2025 NIH study on wearables highlights respiratory tracking for COVID-like events, enabling home isolation with virtual oversight via voice confirmations. This proactive stance prevents 25% of escalations, especially in hospitalized patients using fog computing.
Chronic Disease Management
For diabetes, ML forecasts glucose via continuous sensors, suggesting insulin tweaks—yielding 25% better control and 20% fewer readmits, with voice reminders for meals. Hypertension tools use reinforcement learning to personalize meds, reducing stage 2 cases by 25% through trend analysis.
In heart failure, AI analyzes fluid trends from scales, alerting to decompensation early with 85% sensitivity. PubMed’s 2025 review notes 38% cost savings in CIED patients, extended by conversational AI for behavior change coaching.
Activity Tracking and Fall Prevention
Deep learning classifies motions from accelerometers or cameras, distinguishing walks from stumbles with 95% accuracy, using edge processing for instant feedback. Elders benefit most: AI predicts falls via gait shifts, preventing 40% via preemptive alerts and voice-guided exercises.
Mental Health and Voice Analysis
NLP scans voice for biomarkers like tremor or pace, detecting anxiety with 85% sensitivity in daily interactions. GenAI generates coping scripts, boosting engagement 35% in telehealth, and identifies leading indicators for continuous care.
A 2025 WHO pilot used chatbots for daily mood checks, reducing isolation in seniors by 40% through personalized outreach, complementing wearables for full-spectrum monitoring.
| Application | AI Method | Key Metric | Evidence Source | Inclusivity Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sepsis Prediction | Deep Learning | 90% accuracy, 24-hr lead | NIH 2025 Review | Voice alerts for low-literacy users |
| Diabetes Forecasting | ML Trends | 25% control improvement | PubMed Studies | Personalized voice meal plans |
| Fall Detection | Computer Vision | 95% precision | FDA-Cleared Tools | Non-visual for visually impaired |
| Mood Tracking | NLP/GenAI | 35% engagement rise | WHO Pilots | Culturally adapted speech recognition |
Real-World Case Studies and Evidence
These stories illustrate AI-RPM’s tangible wins, drawn from 2025 deployments and inspired by trials like hospital-at-home programs and voice coaches.
- Biofourmis for Heart Failure: Biofourmis’ platform, FDA-cleared, uses biosensors and ML to monitor 1,000+ patients post-discharge. It predicts exacerbations via vital trends and activity data, achieving 70% readmission reductions and 38% cost savings—$10,000 per patient yearly. Scalable to home care, it integrates EHRs for seamless workflows and adds voice for symptom logging, cutting specialist waitlists.
- Frederick Health’s Chronic Care Program: Targeting 500 COPD/diabetes cases, AI triaged data for personalized plans, including reinforcement learning for med adjustments. 2025 results: Readmissions fell to 2% (vs. 20% national average), saving $2.3 million, with 90% patient satisfaction. Voice prompts enhanced adherence in low-literacy groups, mimicking holistic coaching.
- AlayaCare for Diabetes Monitoring: AlayaCare’s ML suite analyzed 300 users’ wearables, predicting events 11% better while cutting overdiagnoses 54%. ER visits dropped 25%; 2025 expansion to 5,000 includes GenAI for meal plans and federated learning for privacy. Voice integration reached rural users, boosting equity.
- CLEWICU and for Critical Care: CLEWICU’s deep learning forecasts ICU instability 8 hours early, integrating vitals for 85% sensitivity in emergency settings. predicts ventilation needs 24 hours ahead; a PCCP retrained models post-deployment, restoring 92% accuracy across sites. These tools optimize resources, reducing ICU stays by 20%, with edge AI for real-time alerts.
Overcoming Challenges in AI-Driven RPM
Progress demands confronting hurdles—each with proven pathways forward, guided by ethical principles like those in trustmark initiatives.
Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Health data’s sensitivity invites breaches; 2025 saw 700 million records exposed, amplified by voice biometrics. Ethical pitfalls include consent in conversational AI. Solutions: Federated learning keeps data local, while blockchain logs accesses immutably—slashing risks 60%. NIH guidelines stress transparent algorithms and dignity-promoting voice interactions to build trust.
- Voice-Specific Risks: Accent bias; mitigate with diverse training data.
Digital Divide and Accessibility
40% of low-income users lack devices, per WHO, hindering RPM uptake. Voice and SMS AI counters this, reaching 80% more in pilots without broadband. Subsidies and low-bandwidth edges ensure inclusivity, with 2025 FDA pushes for universal designs like text-to-speech for the elderly.
Integration and Reimbursement Issues
EHR silos hinder 50% of implementations; FHIR standards bridge this for smooth data flow. Reimbursement lags—CMS covers 80% but varies by state, with patchwork for SaMD voice tools. Advocacy for AI-specific codes, as in 2025 updates, unlocks funding; developers should align with billing guidance for RPM services.
Addressing AI Bias
Models trained on skewed data err 30% more for minorities, affecting biomarker accuracy. Diverse datasets and audits mitigate;'s retraining cut disparities 25%. Include ethical reviews for voice AI to promote fair outcomes.
| Challenge | Root Cause | Mitigation | Impact | Example Tool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy | Data Exposure | Blockchain/Federated | 60% Risk Drop | Smart contracts for consent |
| Divide | Tech Access | Voice/SMS Tools | 80% Reach Boost | Phone-based NLP |
| Integration | Silos | FHIR Standards | 50% Faster Setup | Cloud APIs |
| Bias | Skewed Data | Diverse Audits | 25% Fairer Outcomes | Inclusive voice datasets |
Future Trends Shaping AI in RPM
Horizons brighten with innovations poised to redefine care, building on public-private partnerships for biomarker growth.
Generative AI and Predictive Tools
GenAI, like LLaMA variants, crafts dynamic plans from biosensors—e.g., postoperative advice with 90% readability via voice. Market: $48 billion by 2030, enhancing telehealth personalization and virtual companionship for seniors.
Integration with 5G and Advanced Sensors
5G enables video RPM with <1ms latency; BioMEMS sensors track biomarkers like cortisol for stress, while voice detects respiratory diseases early (85% accuracy). Expect hybrid wearables for precision medicine support.
Policy and Global Expansion
FDA’s PCCPs ensure adaptive safety; value-based care drives 50% adoption by 2030, with reimbursements expanding for conversational AI. WHO pushes equitable frameworks, targeting 70% low-resource coverage through open-source trustmarks.
Conclusion and Actionable Steps
AI-RPM heralds a patient-centered era: Empowered individuals, unburdened providers, and resilient systems. From crisis to opportunity—addressing shortages, chronic epidemics, and equity gaps—it’s clear: Adoption now saves lives and resources, with conversational AI adding trust and accessibility.
Actionable Steps:
- Assess Readiness: Audit data flows and gaps (1-2 weeks; use free tools like FHIR validators).
- Pilot Targeted: Start with one app for a condition like diabetes, incorporating voice (3 months, track ROI via readmission metrics).
- Build Ethics: Train on bias/privacy with diverse datasets; adopt trustmark guidelines.
- Scale Smart: Integrate FHIR/5G, monitor via PCCPs; evaluate quarterly with patient feedback.
- Partner Up: Collaborate for biomarker research; explore reimbursements under CMS updates.
References
- AAMC. (2024). Physician Shortage Projections.
- WHO. (2025). Global Health Workforce.
- Juniper Research. (2023). Remote Patient Monitoring Forecast (updated 2025).
- Shaik et al. (2023). “Remote Patient Monitoring Using AI: Current State.” WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery.
- LF AI & Data Foundation. (2023). Conversational AI in RPM Report (v2.0). 6-38. Inline sources: NIH/PubMed (e.g., AI-telemedicine reviews), ResearchAndMarkets, Grand View (2025 market data), FDA SaMD guidelines.


 AI Chatbot Development Company
AI Chatbot Development Company AI Software Development Solutions
AI Software Development Solutions Custom NLP Solutions
Custom NLP Solutions Generative AI Development
Generative AI Development Machine Learning Consulting Services
Machine Learning Consulting Services MLOps Consulting Services
MLOps Consulting Services














